Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Fujian Key Lab for Intelligent Processing and Wireless Transmission of Media Information, College of Physics and Information Engineering, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350116, P. R. China
2 Center for Computational Neuroscience, Flatiron Institute, New York 10010, USA
Neurons can be abstractly represented as skeletons due to the filament nature of neurites. With the rapid development of imaging and image analysis techniques, an increasing amount of neuron skeleton data is being produced. In some scientific studies, it is necessary to dissect the axons and dendrites, which is typically done manually and is both tedious and time-consuming. To automate this process, we have developed a method that relies solely on neuronal skeletons using Geometric Deep Learning (GDL). We demonstrate the effectiveness of this method using pyramidal neurons in mammalian brains, and the results are promising for its application in neuroscience studies.
Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2023, 16(6): 2340006
1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所 信息光子学研究室, 陕西 西安 710119
2 中国科学院大学材料科学与光电技术学院, 北京 100049
受限于空间光调制器(SLM)有限的刷新速率,现有的基于SLM的多模光纤(MMF)成像方法并不能满足对活体生物组织内窥成像的需求。考虑到数字微镜器件(DMD)的刷新速率比SLM高两个数量级,因此提出了一种基于DMD二值振幅调制的MMF出射光斑聚焦扫描技术。理论分析表明,MMF出射端任意聚焦区域内的总光强与DMD子区域的振幅调制系数之间存在二次函数关系,因此,通过DMD对MMF入射波前进行二值振幅调制,可实现对MMF出射光斑的聚焦和扫描。对于给定数目的可调制子区域,该二值振幅调制算法的调制次数是基于纯相位迭代优化算法的1/256,是基于三步移相最优相位算法的1/3。基于该技术实现了对长度为5 m、直径为105 μm的MMF出射光斑在三维空间上的聚焦和扫描。研究表明,该技术具有调制速度快、算法可靠性高、聚焦点均匀性好等优点。
成像系统 多模光纤内窥成像 聚焦扫描 二值振幅调制 数字微镜器件 全局最优解
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Research Department of Information Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Department of Electronics Science and Technology, School of Electronic & Information Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
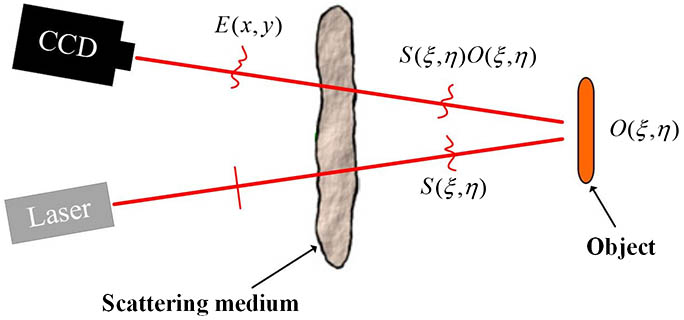
Traditional one-way imaging methods become invalid when a target object is completely hidden behind scattering media. In this case, it has been much more challenging, since the light wave is distorted twice. To solve this problem, we propose an imaging method, so-called round-trip imaging, based on the optical transmission matrix of the scattering medium. We show that the object can be recovered directly from the distorted output wave, where no scanning is required during the imaging process. We predict that this method might improve the imaging speed and have potential application for real-time imaging.
110.0113 Imaging through turbid media 110.1650 Coherence imaging 110.1758 Computational imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 041102





